Town Planning and GIS Engineering
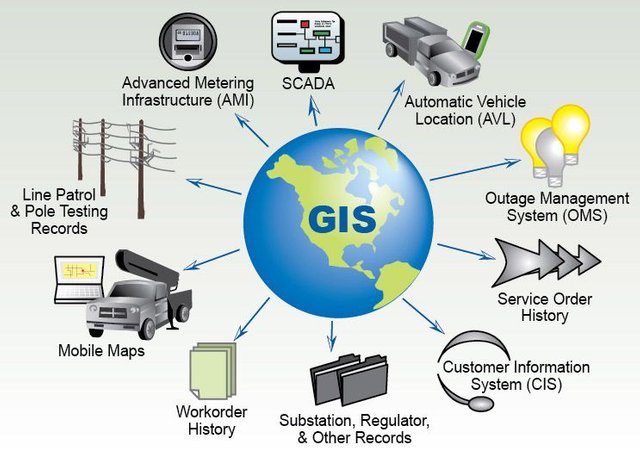
Data Collection and Analysis: GIS technology is used to collect, manage, and analyze spatial data related to land use, infrastructure, demographics, transportation, environmental resources, and other factors relevant to urban planning. This data provides valuable insights into existing conditions and trends within a city or town.
Spatial Planning: GIS is used to create maps and spatial plans that visualize land use patterns, zoning regulations, development proposals, and other spatial information. Planners use GIS tools to assess the spatial relationships between different elements of the urban environment and make informed decisions about land use and development.
Site Selection and Analysis: GIS helps identify suitable locations for various types of development, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or recreational areas. Planners can analyze factors like land availability, accessibility, environmental constraints, and socio-economic considerations to guide site selection decisions.
Infrastructure Planning: GIS is used to plan and design infrastructure systems such as transportation networks, utilities (water, sewer, electricity), parks, and green spaces. Planners can use GIS to assess existing infrastructure assets, identify areas in need of improvement or expansion, and optimize the layout and design of new infrastructure projects.
Environmental Management: GIS technology is used to assess and manage environmental resources within urban areas, including natural habitats, water bodies, air quality, and green infrastructure. Planners use GIS to identify environmentally sensitive areas, develop conservation strategies, and mitigate the impacts of urban development on the environment.
Community Engagement: GIS facilitates public participation in the planning process by providing interactive maps and online tools that allow residents to explore planning proposals, provide feedback, and participate in decision-making. Planners use GIS-based public engagement platforms to solicit input from diverse stakeholders and build consensus around planning decisions.
Policy Development: GIS supports evidence-based policy development by providing spatial analysis tools that help planners evaluate the potential impacts of policy interventions and assess alternative scenarios. Planners use GIS to model land use changes, assess policy effectiveness, and inform long-term strategic planning initiatives.
Emergency Management: GIS technology is used in emergency management and disaster response to assess risk, plan evacuation routes, coordinate response efforts, and support recovery efforts. Planners use GIS-based tools to map hazard zones, identify vulnerable populations, and develop emergency preparedness plans.
